Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
Longitudinal and Transverse Waves: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Transverse and Longitudinal Waves, Wave Pulse and Continuous Waves, Phase Lag in Waves & Particle and Wave Velocity etc.
Important Questions on Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
An electromagnetic wave is travelling in a medium with a velocity . The electric field oscillations, of this electromagnetic wave wave, are along the y – axis.
(a) Identify the direction in which the magnetic field oscillations are taking place, of the electromagnetic wave wave.
(b) How are the magnitudes of the electric and magnetic fields in the electromagnetic wave related to each other?
A sound wave propagating along , in mediumof density is transmitted to a mediumof density . The equation of excess pressure developed by wave in mediumand that in medium respectively are (in SI unit) and (in SI units)
Then the ratio of intensity of transmitted wave (wave in medium) to the intensity of incident wave that is is
A transverse harmonic wave on a string is given by where and are in and in . The wave velocity is _________ .
The engine of a train moving with speed towards a platform sounds a whistle at frequency . The frequency heard by a passenger inside the train is: (Neglect air speed. Speed of sound in air )
Energy is not propagated by which of the following waves?
A heavy rope is suspended from a rigid support. A wave pulse is set up at the lower end; then:
Two harmonic waves travelling in the same medium have frequency in the ratio and intensity in the ratio . Their amplitude ratio is
Two waves of equal amplitude when superposed, give a resultant wave having an amplitude equal to that of either wave. The phase difference between the two waves is
The wave number of the microwaves with wavelength .
Two pulses and have instantaneous velocities as shown by arrows. In which direction do these pulses travel in time?
A wave pulse in a horizontal string is represented by a function
(c. g .s system) then
The equation of standing wave in a stretched string is given by , where and are in and in sec. Calculate the ratio of wave speed to the particle speed.
The differential equation of displacement of a wave is
Given that phase difference between oscillation of sources as , and medium of width is kept in between and . Where the speed of sound is . Speed of sound and wavelength in air is and respectively. If the phase difference between the waves at point is . Find the value of
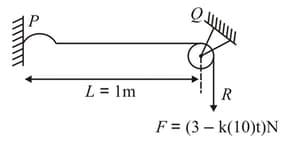
As shown in figure string is stretched by force where is a constant and is time in second. At time a pulse is generated at the end of the string. Find the value of if the value of force become zero as the pulse reaches at point (Assume linear mass density is constant and having value
Two pulses travelling on the same string are describes by the function and ,generated from points and is in meter respectively where (in metre) and (in sec) are in the distance between is The position where these two pulses will meet from is. (Shape of the pulse does not change) is Find

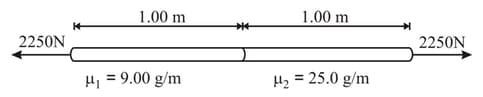
A wire is made by welding together two metals having different densities. Figure shows a long section of wire centred on the junction, but the wire extends much farther in both direction. The wire is placed under tension, then a wave with an amplitude of is sent down the wire. How many wavelengths (complete cycles) of the wave are in this long section of the wire ?
The equation of a travelling wave is given by , where and are in metre and is in second. The velocity of wave is
For a three-dimensional wave represented by
The direction of is
Which one of the following is an example of a one-dimensional wave?
